IMDG Code:
The IMDG code is a very much living document and gets amended from time to time (every 2 years). In the last decade major changes were made to Ems-emergency medical schedule, MFAG and INF codes (carriage of nuclear materials).
IMDG Code means the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code adopted by the Maritime Safety Committee of the Organization by resolution MSC.122(75)
The objective of the IMDG Code is to enhance the safe carriage of dangerous goods while facilitating the free unrestricted movement of such goods and prevent pollution to the environment.
INTERNATIONAL MARITIME DANGEROUS GOODS CODE:
- It gives a uniform international code of dangerous goods for transportation by sea.
- It gives methods of packing in packets or in container, stowage and segregation of incompatible substances.
Legal status of IMDG code:
- The IMDG code is a legal document under chapter VII part A of SOLAS 1974 as amended.
- Regulation VII/1.3 prohibits the carriage of dangerous goods by sea except when carried in accordance with the IMDG code.
- MARPOL 73/78, annex III, regulation 1(2) prohibits the carriage of harmful substances in ships except when carried in accordance with the IMDG code.
Application and implementation of IMDG Code:
- The provisions contained in this Code are applicable to all ships to which the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea, 1974 (SOLAS 74), as amended, applies and which are carrying dangerous goods as defined in regulation 1 of part A of chapter VII of that Convention.
The provisions of regulation II-2/19 of that Convention apply to passenger ships and to cargo ships constructed on or after 1 July 2002. For:
- A passenger ship constructed on or after 1 September 1984 but before 1 July 2002; or
- A cargo ship of 500 gross tons or over constructed on or after 1 September 1984 but before 1 July 2002; or
- A cargo ship of less than 500 gross tons constructed on or after 1 February 1992 but before 1 July 2002,
- For cargo ships of less than 500 gross tons constructed on or after 1 September 1984 and before 1 February 1992, it is recommended that Contracting Governments extend such application to these cargo ships as far as possible.
- All ships, irrespective of type and size, carrying substances, material or articles identified in this Code as marine pollutants are subject to the provisions of this Code.
The aim of IMDG code is:
- To regulate the transport by sea of dangerous goods to reasonably prevent injury to person or damage to the ship.
- To regulate transport by sea of marine pollutant to prevent harm to the marine environment.
The contents of IMDG code:
- The code is composed of 7 parts. The code is presented in two books, volume 1 and volume 2.
- It is necessary to use both books to obtain the required information when shipping dangerous goods by sea.
Volume – 1
Part – 1: General provision, definitions and training.
Part – 2: Classification.
Part – 4: Packing and tank provision.
Part – 5: Consignment procedure.
Part – 6: Construction and testing of packings intermediate bulk containers, large packing portable tanks and road tank vehicles.
Part – 7: Provision concerning transport operation.
Volume – 2
Part – 3: Dangerous goods list and limited quantity exceptions.
The Dangerous Goods List is the central core of the IMDG Code and presents information on the transport requirements for all dangerous goods in a coded form.
Following are the supplements of IMDG code:
- EMS guide – emergency reponse procedures for ships carrying dangerous goods.
- MFA guide – medical first aid guide for using accidents envolving dangerous goods.
- Reporting procedures
- IMO / ILO / UN number for packing cargo transport units.
- Recommendations on the safe use of the pesticides in ships.
- INF code – International code for the safe carriage of packaged irradiated nuclear fuel ,
- Plutonium and high level radioactive waves on board ships.
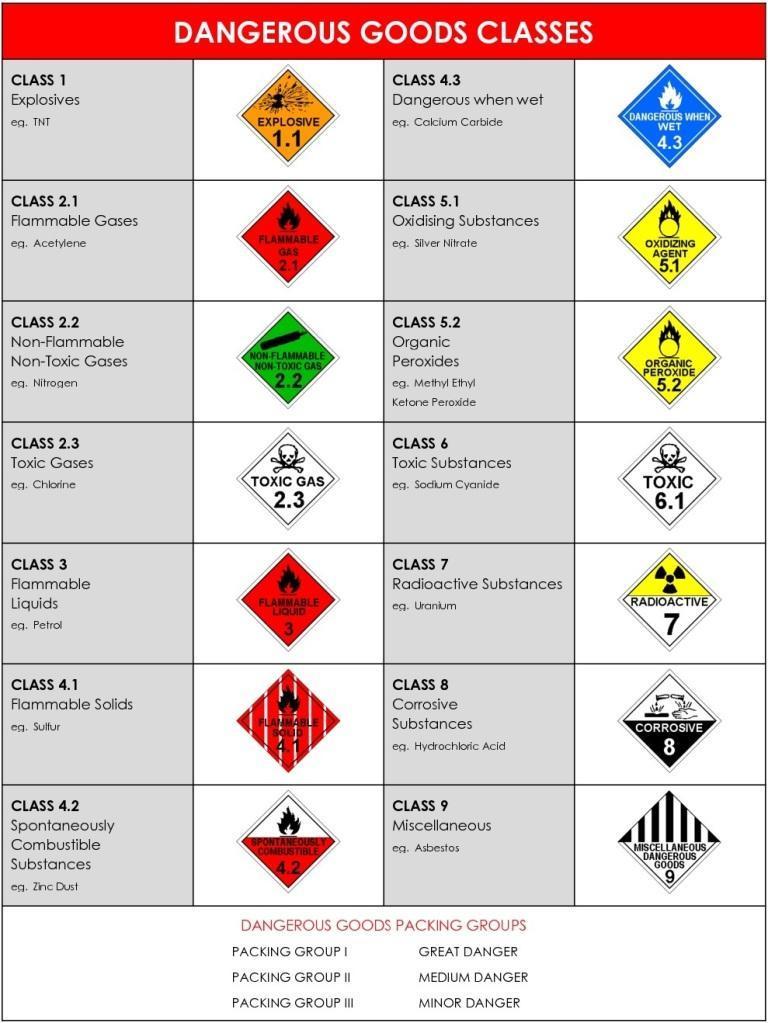
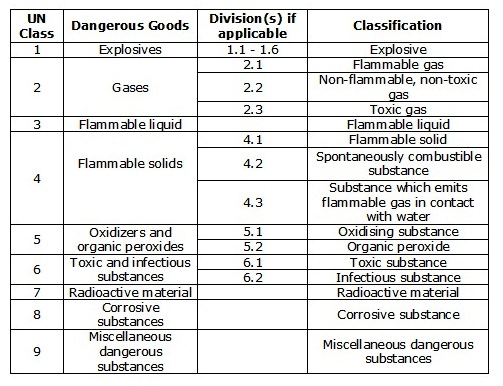
Classes of Dangerous Cargo are:
Class 1: Explosives
Division 1.1: substances and articles which have a mass explosion hazard
Division 1.2: substances and articles which have a projection hazard but not a mass explosion hazard
Division 1.3: substances and articles which have a fire hazard and either a minor blast hazard or a minor projection hazard or both, but not a mass explosion hazard
Division 1.4: substances and articles which present no significant hazard
Division 1.5: very insensitive substances which have a mass explosion hazard
Division 1.6: extremely insensitive articles which do not have a mass explosion hazard.
Class 2: Gases
Class 2.1: flammable gases
Class 2.2: non-flammable, non-toxic gases
Class 2.3: toxic gases
Class 3: Flammable liquids
Class 4: Flammable solids; substances liable to spontaneous combustion; substances which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases
Class 4.1: flammable solids, self-reactive substances and solid desensitized explosives
Class 4.2: substances liable to spontaneous combustion
Class 4.3: substances which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases.
Class 5: Oxidizing substances and organic peroxides
Class 5.1: oxidizing substances
Class 5.2: organic peroxides
Class 6: Toxic and infectious substances
Class 6.1: toxic substances
Class 6.2: infectious substances
Class 7: Radioactive material
Class 8: Corrosive substances
Class 9: Miscellaneous dangerous substances and articles
The numerical order of the classes and divisions is not that of the degree of danger.
Class 10: Marine pollutants
Marine pollutants shall be classified in accordance with chapter 2.9.3 in IMDG Code.
The documents required for carriage of IMDG cargo are:-
- Shipping declaration
- Document of compliance
- Dangerous goods manifest
Objective of IMDG Code:
- Enhance the safe carriage of dangerous goods by all modes of transportation.
- Facilitate free and unrestricted movement.
- Bring worldwide uniformity in their carriage regulations.
- Prevent injury to personnel.
- Prevent damage to ship and her cargoes.
- Regulate the carriage of marine pollutant so as to prevent damage to marin environment.
Shipper’s Declaration of Dangerous Goods:
The legislation requires a declaration from the consignor (shipper) stating that the goods declared are classified and packed correctly and also a declaration from the person packing the container that it has been done so correctly, these are Dangerous Goods Declaration and the Container Packing Certificate.
These declarations may be in any format, but must be in accordance with the regulations of the IMDG code, Chapter 5.4 refers (an example is given below) Often, the Dangerous Goods Declaration is combined with the Container Packing Certificate into one document, generally known as the Multimodal Dangerous Goods Form.
These documents can also known as Dangerous Goods Note (DGN), Dangerous Goods Declaration (DGD), Multimodal Dangerous Goods Form (MDGF), Shippers Declaration, and Dangerous Cargo Declaration (DCD)
The information required on the documents is as follows:
Shipper – full name and address
Consignee – full name and address
Description of goods in sequence
a) UN number (preceded by UN)
b) Proper Shipping Name including technical name (if required)
c) Primary IMO class, secondary, tertiary
d) Packing Group
Information which supplements the Proper Shipping Name in the dangerous goods description (If applicable)
- Technical names for “n.o.s.” and other generic descriptions
- Empty uncleaned packagings, bulk containers and tanks
- Wastes
- Elevated temperature substances
- Marine Pollutants
- Flashpoint
- Mass kg gross/ net
In addition to the dangerous goods description the following information shall be included after the dangerous goods description on the dangerous goods transport document.
Total quantity of dangerous goods: – This includes the weight in Kilos of each substance, as well as the number and type of packaging.
Also to be included if applicable;
- Limited quantities
- Salvage packagings
- Substances stabilized by temperature control
- Control and Emergency temperature: ….° C
- Aerosols – If the capacity of an aerosol is above 1000ml, this shall be declared.
Statement: “Dangerous goods being transported have been packed, labeled & declared in accordance with standard international shipping regulation & IMDG code”
Segregation of Dangerous Goods:
This section has tables for following:
- Segregation for dangerous goods carried in packaged form: this is given in the form of a table. Stating the type of segregation required between classes of cargo, excluding class 1, which has an altogether separate table. The terms used for segregation are:
| Away from: Effectively segregated so that the incompatible goods cannot interact dangerously in the event of an accident but may be transported in the same compartment or hold or on deck, provided a minimum horizontal separation of 3 m, projected vertically, is obtained. | 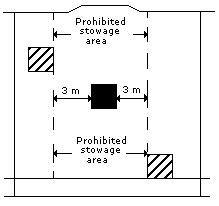 |
| Separated from: In different compartments or holds when stowed under deck. Provided the intervening deck is resistant to fire and liquid, a vertical separation, i.e., in different compartments, may be accepted as equivalent to this segregation. For on deck stowage, this segregation means a separation by a distance of at least 6 m horizontally. | 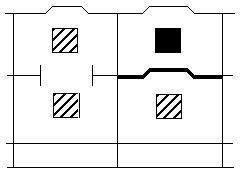 |
| Separated by a complete compartment or hold from: Either a vertical or a horizontal separation. If the intervening decks are not resistant to fire and liquid, then only a longitudinal separation, i.e., by an intervening complete compartment or hold, is acceptable. For on deck stowage, this segregation means a separation by a distance of at least 12 m horizontally. The same distance has to be applied if one package is stowed on deck, and the other one in an upper compartment. | 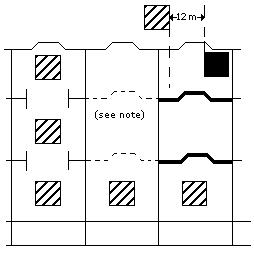 Note: One of the two decks must be resistant to fire and to liquid. |
| Separated longitudinally by an intervening complete compartment or hold from: Vertical separation alone does not meet this requirement. Between a package under deck and one on deck, a minimum distance of 24 m, including a complete compartment, must be maintained longitudinally. For on deck stowage, this segregation means a separation by a distance of at least 24 m longitudinally. | 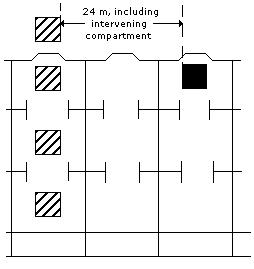 |
Legend
| Reference package. . . . . . . . . . |  |
| Package containing incompatible goods . . . |  |
| Deck resistant to fire and liquid. . |  |
Note: Vertical lines represent transverse watertight bulkheads between cargo spaces.
- For containers the table is the same as above but the meaning of the above segregation terms is different.
- For hatch coverless type container vessel, the table is again the same but the meanings of the above segregation terms are different.
- There is a separate table for ro-ro vessel.
- Separate table for segregation between cargo in bulk and cargo in packaged form.
- Segregation table for class 1 cargo which is by compatibility codes. Which are A to L, N and S.
Precautions while Loading/ Carrying/ Discharging Dangerous Goods:
- “No Smoking” signs to be put up & strictly enforced.
- “No naked lights” permitted on the deck or in the holds.
- Fire hoses to be rigged, fire main charged & other fire fighting apparatus kept in a constant state of readiness.
- Spark arresters to be fitted over the funnel, galley – exhausts & hold ventilators.
- No hot work, chipping or painting to be in progress on deck to avoid creating sources of ignition.
- Flashlights, walkie-talkies etc. to be intrinsically safe.
- No oily waste, wood, rope, gunny, etc, to be left in hold or on deck where it can catch fire by spontaneous heating.
- Fire patrol & gangway watches to be maintained.
- Refer to the IMDG Code & findout the particulars for the cargo to be loaded with regards to hazards (compatibility, stowage, segregation)
- The appropriate international code of signals by day & by night is to be displayed.
- No bunkering operation is to be carried out during loading or discharging.
- Wireless transmission should not be done of voltage exceeding 50 volts.
- Radar should not be operated during loading or discharge.
- Forklifts should not be used in the vicinity of dangerous goods.
- Loading is to be suspended if inclement weather threatens.
- Defective packages should not be accident.
- Port regulation is to be complied.
- Explosive must be stowed in a magazine, which is a woodlined compartment, sometimes specially constructed to stow explosives safely.
- No electric cables should pass through the magazine, if this is unavoidable, the cable should be sheathed by an approved, sealed, non combustible barrier & tested before loading.
- Explosive are unstable when wet & should be stowed in a cool, dry, well ventilated space away from hot bulkhead or decks.
- Electrical fittings must be disconnected in compartments containing dangerous goods.
- Ventilation fans to the space must be flame-proof, if not disconnected.
- Explosives must be stowed away from living quarters.
- Masts must be fitted with an efficient lightning conductor as lightning presents a grave danger.
Precautions to be taken if Cargo has to be carried under Fumigation:
Cargo transport units loaded without ventilation after fumigation (fumigation in transit):- When a cargo transport unit under fumigation is taken on board ship without preliminary ventilation, it shall be transported as FUMIGATED CARGO TRANSPORT UNIT, UN 3359, Class 9 in accordance with the provisions of the IMDG Code.
- The following special precautions apply to ship-side operations:
- A fumigated cargo transport unit shall not be allowed on board until a sufficient period has elapsed to attain a reasonable uniform gas concentration throughout the cargo in it. Because of variations due to types and amounts of fumigants and commodities and temperature levels, the period between fumigant application and loading of the fumigated unit on board the ship shall be determined by the competent authority. Twenty-four hours is normally sufficient for this purpose. Before loading the cargo transport unit should be checked for leaks and any leakage sealed.
- The master shall be informed prior to loading of fumigated cargo transport units under fumigation. These shall be identified with the warning mark, incorporating the fumigant name and the date and time of fumigation.
- The special list/manifest/stowage plan shall identify the fumigated cargo transport units and indicate their stowage location on board. The transport document for fumigated cargo transport units shall indicate the date of fumigation and the type and amount of fumigant used.
- Stowage category B has been assigned to UN 3359; however, on deck stowage is preferred. In addition, it shall be stowed clear of living quarters and should be 6 m away from vent intakes.
- If stowed under deck, the cargo space should be equipped with mechanical ventilation sufficient to prevent the build-up of fumigant concentrations above the toxicity levels (threshold limits) set out by competent authorities. The threshold limit for occupational exposure to the fumigant can be found on the Safety Data Sheet if available. The ventilation rate of the mechanical ventilation system should be at least two air changes per hour, based on the empty cargo space.
- If stowed under deck, equipment suitable for detecting the fumigant gas or gases used shall be carried on the ship, with instructions for its use.
- Before a fumigated cargo transport unit is loaded to a ship under deck, special precautions are necessary. This should include the following:
- At least an officer and one other are to receive appropriate training and will be designated as the trained representatives of the master. The master, through his representative, is responsible for ensuring safe conditions in the occupied spaces of the ship; and
- The trained representatives should brief the crew before the fumigated cargo transport unit is loaded.
- Most fumigant gases are heavier than air so care should be taken in the holds particularly when working on the tank tops.
- The trained representatives of the master should be provided, and be familiar, with:
- The information in the relevant Safety Data Sheet (SDS), if available; and
- The recommendations of the fumigant manufacturer concerning methods of detection of the fumigant in air, its behaviour and hazards properties, symptoms of poisoning, relevant first aid and special medical treatment and emergency procedures.
- The ship should carry:
- appropriate gas-detection equipment for the fumigant concerned, together with instructions for its use when the fumigated cargo transport unit is stowed under deck;
- instructions on disposal of residual fumigant material; and
- emergency response information regarding UN 3359 such as a copy of the latest version of the Medical First Aid Guide for Use in Accidents Involving Dangerous Goods (MFAG).
In addition, the ship should carry at least four sets of appropriate respiratory protective equipment, and, when the fumigated cargo transport unit is stowed on deck, appropriate gas detection equipment for the fumigant concerned, together with instructions for its use.
- Prior to the arrival of the ship, generally not less than 24 hours in advance, the master should inform the appropriate authorities of the country of destination and ports of call that fumigation in transit is being carried out. The information should include the type of fumigant used, the date of fumigation and cargo spaces carrying fumigated cargo transport units.
Dangerous Goods Manifest:-
- The carrier, its agents, and any person designated for this purpose by the carrier or agents must prepare a dangerous cargo manifest, list, or stowage plan. This document may not include a material that is not subject to the requirements of the Hazardous Material Regulations or the IMDG Code. This document must be kept on or near the vessel’s bridge, except when the vessel is docked in a United States port. When the vessel is docked in a United States port, this document may be kept in the vessel’s cargo office or another location designated by the master of the vessel provided that a sign is placed beside the designated holder on or near the vessel’s bridge indicating the location of the dangerous cargo manifest, list, or stowage plan. This document must always be in a location that is readily accessible to emergency response and enforcement personnel. It must contain the following information:
(1) Name of vessel and official number. (If the vessel has no official number, the international radio call sign must be substituted.);
(2) Nationality of vessel;
(3) Shipping name and identification number of each hazardous material on board as listed in as listed in the IMDG Code and an emergency response telephone number.
(4) The number and description of packages (barrels, drums, cylinders, boxes, etc.) and gross weight for each type of package;
(5) Classification of the hazardous material in accordance with either:
(i) The Hazardous Materials Table, or
(ii) The IMDG Code.
(6) Any additional description required.
(7) Stowage location of the hazardous material on board the vessel.
(8) In the case of a vessel used for the storage of explosives or other hazardous materials, the following additional information is required:
(i) Name and address of vessel’s owner;
(ii) Location of vessel’s mooring;
(iii) Name of person in charge of vessel;
(iv) Name and address of the owner of the cargo; and
(v) A complete record, by time intervals of one week, of all receipts and disbursements of hazardous materials. The name and address of the consignor must be shown against all receipts and the name and address of the consignee against all deliveries.
(b) The hazardous material information on the dangerous cargo manifest must be the same as the information furnished by the shipper on the shipping order or other shipping paper, except that the IMO “correct technical name” and the IMO class may be indicated on the manifest as provided in paragraphs (a)(3) and (a)(5) of this section. The person who supervises the preparation of the manifest, list, or stowage plan shall ensure that the information is correctly transcribed, and shall certify to the truth and accuracy of this information to the best of his knowledge and belief by his signature and notation of the date prepared.
(c) The carrier and its agents shall insure that the master, or a licensed deck officer designated by the master and attached to the vessel, or in the case of a barge, the person in charge of the barge, acknowledges the correctness of the dangerous cargo manifest, list or stowage plan by his signature.
(d) For barges, manned or unmanned, the requirements of this section apply except for the following:
(1) In the case of a manned barge, the person in charge of the barge shall prepare the dangerous cargo manifest.
(2) In the case of an unmanned barge, the person responsible for loading the barge is responsible for the preparation of a dangerous cargo manifest, list, or stowage plan and must designate an individual for that purpose.
(3) For all barges, manned or unmanned, the dangerous cargo manifest must be on board the barge in a readily accessible location and a copy must be furnished to the person in charge of the towing vessel.
(e) Each carrier who transports or stores hazardous materials on a vessel shall retain a copy of the dangerous cargo manifest, list, or stowage plan for at least one year, and shall make that document available for inspection.
IMDG code: Excepted Quantities:

The excepted quantity is the maximum quantity per inner and outer packaging for transporting dangerous goods as excepted quantities. The quantity limit can be found in the column 7b of the Dangerous Goods List. 7b does not directly list the max quantity per inner and outer packaging. Instead, 7b gives various E codes (E0~E5).
IMDG code: Limited Quantities:
Limited quantities –

The limited quantity is the maximum quantity per inner packaging or article for transporting dangerous goods as limited quantities. It can be found in the column 7a of Dangerous Goods List. In the example below, the limited quantity for antimony compounds is 5kg per inner packaging.
IMDG code: Compatibility Group:
Compatibility group refers to a designated alphabetical letter used to categorize different types of Class 1 explosive substances and articles for purposes of safe stowage and segregation.
Document of Compliance (SOLAS II-2/54.3) pertaining to dangerous goods:
- The administration shall provide the ship with an appropriate document of evident of compliance of construction & equipment with the requirements of this regulation, Reg.19 of SOLAS 54, Chp. II-2, as amended.
- Certification for dangerous goods, except solid dangerous goods in bulk is not required for those cargoes specified as class 6.2 & 7 as defined in reg. VII/2 and dangerous goods in limited quantities.
- The document of compliance shall also contain information indicating class wire allowable locations for stowage of dangerous goods in packaged form onboard.
SOLAS Chapter VII – Part A – Carriage of Dangerous Goods in Packaged Form:-
Application:-
- Unless expressly provided otherwise, this part applies to the carriage of dangerous goods in packaged form in all ships to which the present regulation apply and to cargo ships of less then 500 GrT.
- The provisions of this port do not apply to ship’s stores & equipments.
- The carriage of dangerous goods in packaged form is prohibited, except in accordance of this chapter.
- To supplement the provisions of this part, each contracting government shall issue detailed instructions on EMS & Medical First Aid to be provided, relevant to incidents involving Dangerous Goods in Packaged form, taking into account the guidelines, viz EMS Guide & MFAG Guide, developed by the organisation.
Requirements for Carriage of Dangerous Goods:-
- The carriage of Dangerous Goods in packaged form shall be in compliance with the relevant provisions of the IMDG code.
Documentation:-
- In all documents relating to the carriage of Dangerous Goods in packaged form by sea, the Proper Shipping Name shall be used (trade name, alone shall not be used) and the correct description given in accordance with the classification set out in the IMDG code.
- The transport documents prepared by the shipper shall be accompanied with a signed certificate or a declaration, stating that the consignment offered for shipment is properly packed, marked & labelled or placarded as appropriate and in proper condition for carriage.
- The person responsible for packing / loading of dangerous goods in CTU shall provide a singed container / vehicle packing certificate stating that the cargo in the unit has been properly packed and secured and that all applicable transport requirements have been met.
- Where there is due cause to suspect that a Cargo Transport Unit (CTU) in which the Dangerous Goods are packed in compliance with the requirements of par (2) & (3) above such CTU shall not be accepted the carriage.
- Each ship carrying Dangerous Goods in packaged form shall have a special list or manifest setting forth, in accordance to the locations there of. A copy of these documents, shall be made available before departure to the person or organisations designated by the port state authority.
Cargo Securing Manual:-
- Cargo, Cargo Units & Cargo Transport Unit’s shall be loaded, stowed & secured throughout the voyage in accordance with the Cargo Securing Manual approved by the Administration. (more info)
Reporting of Incidents involving Dangerous Goods:-
- When an incident takes place involving the loss or likely loss overboard of dangerous goods in packaged form into the sea, the master or other person having charge of the ship shall report the particulars of such an incident without delay and to the fullest extent to nearest coastal state.
- The report shall be drawn up based on general principles & guidelines developed by the organisation.
M.S. Act Sec.331:-
- The Central Government may make rules for regulating in the interest of safety, the carriage of dangerous goods in ships.
- In particular and without prejudice to the generally of the foregoing power, such rules may provide for the classification, packing, labelling & marking of such goods (whether with or w/o other cargo), including the plan for stowing, the fixing of the maximum quantity of any such class of goods which may be carried in different ships or classes of ships.
- The owner, master or agent of a ship carrying or intending t carry any dangerous goods as cargo and about to make a voyage from a portion. India, shall furnish in advance the prescribed particulars of the ship and the cargo to such authority as may be prescribed for the purpose.
- A surveyor may inspect the ship for the purpose of securing that any rules under this section are complied with.
- If any rules made in pursuance of the section is not complied with in relation to any ship, the ship shall be deemed for the purpose of this part to be an unsafe ships.
- This section shall apply in the same manner as it applies to Indian Ships, to ships other than Indian Ships while they are within any part in India or are embarking or disembarking passengers or are loading or discharging cargo or fuel within Indian Jurisdiction.
Explanation:-
Expression “Dangerous Goods” means goods which by reason of the nature, quantity or mode of stowage are either singly or collectively liable to endanger the life or health of persons or near the ship or to imperil the ship and includes all substances within the meaning of expression, explosion as defined in the Indian Explosive Act. 1884, and any other goods which the Central Government may be notification in the official Gazette, specify as dangerous goods.
Types of Magazines for Carriage of Explosives:
Magazine Stowage for Explosives:
- Magazine means a closed cargo transport unit or a compartment in the ship designed to protect certain goods of class 1 from damage by other cargo during loading & unloading and adverse weather conditions when in transit & to prevent unauthorised access.
- The stowage of explosive substances and certain articles is subjected to varying levels of containment when stowed below deck are primarily defined as Magazine Stowage Type “A”, “C” & “Special Stowage.
Magazine Stowage Type “A”:
- Stowage applies to those substances which shall be kept clear of steel works.
- The innerside & floors of compartment are close boarded with wood (covered with wood).
- The shipside should also be free of rust and should be covered with battens placed not more than 150mm apart.
- Roof or deck-head clean and free of rust. However, it need not be battened.
- The top of the stow atleast 300 mm clear of deck-head.
- Guards against friction between any spilled contents & packages.
- Packaging requiring magazine, Type “A” stowage shall have no exposed external parts made of ferrous metal or aluminium alloy.
- One or more doorway, atleast 1.2m wide, should be fitted facing the hatchway.
Magazine Stowage Type “C”:
- Means a closed cargo transport unit positioned as nearly as practicable to the C/L of the ship.
- It shall not be positioned closer to the ship’s side than a distance equal to one-eight of the beam or 2.4m whichever is lesser.
Special Stowage:
- Goods of Class 1 (Explosives), allocated to this category shall be stowed as far as practicable from living quarters.
- Closed CTU’s used for goods of this category shall not be positioned closer to the ships side then a distance equal to 1/8 of beam or 2.4m whichever is lesser.
- This stowage is allocated to certain articles of which the principal hazard is that of fire accompanied by dense smoke & tear. (Compatibility group G, H or K) and also substance presenting special risk (compatibility group L).
- A steel CTU which prevent leakage of contents shall be used for this purpose.
- Goods of only one compatibility group shall be stowed in any one compartment.
- When separate compartments are not available, the competent authority may allow goods in compatibility group G & H to be stowed in the same compartment not less than 3m apart, stowed in separate steel magazines.
IMDG Code: Labels / Placards:
The IMDG Code recommends a system based on labels and placards designed especially so that all who work close to this type of cargo will be able to recognize, preferably at first sight, the nature of the risks entailed by these substances, whatever their packaging might be.
Labels: –
The IMDG Code states that all packaging, packages and drums carrying dangerous goods must be labelled. The labels are in the shape of a rhombus in white, orange, blue, green or red, or a combination of these colours. Symbols illustrating the danger of the class are also required. In general, each label is divided into two parts, the bottom half and the top half. The top half is for the symbol of the class of the good(s), and the lower half is for the text, class or division number. The minimum dimensions of labels are 10 cm x 10 cm. Labels must be firmly adhered to and placed on the package so that it can easily be seen. The quality of the labels must be such so they do not deteriorate outdoors and remain unaltered during the complete transport period and at least three months in the sea. Due to the fact that dangerous goods can pose more than one risk, it is also necessary to use “secondary risk labels”. These labels are the same as the ones showing the primary risk, regarding their colour, shape and symbols. Even though the IMDG Code says nothing to this effect, in some countries the class number is only indicated in the primary risk label, and that the secondary risk label does not include the class number. This is an effective way to distinguish between both.
Placards: –
The IMDG Code determines that all “cargo transport units” containing dangerous goods must be placarded. In this context, cargo transport units are containers, containers for liquids, tank vehicles, vehicles transporting goods by land, railway wagons with water tanks, good tanks destined for intermodal transport. Placards have the same shape, colours and symbols as the labels, but their dimension is 25 x 25 cm. Containers carrying more than 4000 kilograms of dangerous goods, and all tanks for liquids and gases must have the “United Nations number”. The UN number has four digits and is the number assigned by the United Nations to all goods identified and classified as dangerous.
- Containers carrying dangerous goods must display at least one placard on each side and one on each end of the unit (this is to say, on its four sides).
- Rail wagons must be placarded on at least both sides.
- Freight containers, semi-trailers and portable tanks must be placarded on all four sides.
- Road vehicles must display appropriate placards on both sides as well as the rear.
Hazardous Materials Warning Placards:-
| CLASS 1 Explosives  *Enter Division Number 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 and compatibility group letter, when required. Placard any quantity. | CLASS 1.4 Explosives  *Enter compatibility group letter, when required. Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more. | CLASS 1.5 Explosives  *Enter compatibility group letter, when required. Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more. | CLASS 1.6 Explosives  *Enter compatibility group letter, when required. Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more. | CLASS 2 OXYGEN  Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more, gross weight of either compressed gas or refrigerated liquid. |
| CLASS 2 FLAMMABLE GAS  Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more. | CLASS 2 NON-FLAMMABLE GAS  Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more, gross weight. | CLASS 2 POISON GAS  Placard any quantity 2.3 material. | CLASS 3 FLAMMABLE  Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more. | CLASS 3 GASOLINE  May be used in the place of FLAMMABLE on a placard displayed on a cargo tank or a portable tank being used to transport gasoline by highway. |
| CLASS 3 COMBUSTIBLE  Placard a combustible liquid when transported in bulk. see §172.504(f)(2) for use of FLAMMABLE placard in place of COMBUSTIBLE placard. | CLASS 3 FUEL OIL  Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more. | CLASS 4 FLAMMABLE SOLID  Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more. | CLASS 4 SPONTANEOUSLY COMBUSTIBLE  Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more. | CLASS 4 DANGEROUS WHEN WET  Placard any quantity of Division 4.3 material. |
| CLASS 5 OXIDIZER  Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more. | CLASS 5 ORGANIC PEROXIDE  Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more. | CLASS 6 KEEP AWAY FROM FOOD  Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more. | CLASS 6 POISON  Placard any quantity of 6.1, PGI, inhalation hazard only. Placard 454 kg (1,001 lbs) or more of PGI or II, other than PGI inhalation hazard. | CLASS 7 RADIOACTIVE  Placard any quantity of packages bearing the RADIOACTIVE III label. Certain low specific activity radioactive materials in “exclusive use” will not bear the label, but RADIOACTIVE placard is required. |
| CLASS 8 CORROSIVE  Placard 454 kg (1,001lbs) or more. | CLASS 9 miscellaneous  Not required for domestic transportation. Placard 454 kg (1,000 lbs) or more gross weight of a material which presents a hazard during transport, but is not included in any other hazard class. | DANGEROUS Placard 454 kg (1,001 lbs) gross weight of two or more categories of hazardous materials listed in Table 2. A freight container, unit load device, motor vehicle, or rail car which contain non-bulk packagings with two or more categories of hazardous materials that require placards specified in Table 2 may be placarded with a DANGEROUS placard instead of the separate placarding specified for each of the materials in table 2. However, when 2,268 kg (5,000 lbs) or more of one category of material is loaded at one facility, the placard specified in Table 2 must be applied. | SUBSIDIARY RISK PLACARD  Class numbers do not appear on subsidiary risk placard. | |
RAIL  Placard empty tank cars for resident of material last contained. |  Required background for placard on rail shipments of certain explosives and poisons. Also required for highway route controlled quantities of radioactive materials. (see §172.507 and 172.510). |  IMDG – Hazardous Materials Warning Placards – UN or NA identification numbers IMDG – Hazardous Materials Warning Placards – UN or NA identification numbers |
IMDG code Vol1 chapter 7.2 on Segregation gives all the information on segregation.
Separated longitudinally by an intervening complete compartment or hold from: – Vertical separation alone does not meet this requirement. Between a package under deck and one on deck, a minimum distance of 24 metres, including a complete compartment, must be maintained longitudinally. For on deck stowage, this segregation means a separation by a distance of at least 24 metres longitudinally.
Hazards associated with IMDG cargo & Precautions to be taken while Loading Dangerous Goods in Packaged Form:
Dangerous goods are assigned to different classes depending on their predominant hazard. The UN classifies dangerous goods in the following classes and, where applicable, divisions:
PRECAUTIONS WHEN LOADING / UNLOADING DANGEROUS GOODS:-
- Documentation in order (shipper’s declaration, container packing certificate, emergency information) emergency information).
- All cargo operations supported by a responsible officer who should be in possession of operational and emergency information (including stability information)
- No intoxicated person to be allowed charge of operation,
- No unauthorized person allowed in vicinity of cargo being handled,
- Compartment dry and suitable for cargo,
- Cargo handling equipment checked before use,
- No cargo handling under adverse weather conditions,
- Packaging and segregation as per IMDG code,
- All cargo properly labelled, no labels defaced or removed,
- Cargo handled carefully, handling kept to minimum,
- Tanks not overfilled,
- Port authority informed,
- Fire wires rigged as necessary,
- Emergency equipment available for fire / spillage,
- Suitable precautions against fire and explosion,
- Packages to be stowed as planned in accordance with the IMDG code,
- Cargo space to be properly ventilated,
- ‘B’ flag displayed,
- There is a safe access to the packages, so that in case of fire they can be removed,
- Electrical fitting in good condition.
- The package is properly labelled / marked and placarded.
- If cargo in drums, they should be stowed vertically,
- The cargo should be placed in such a manner that there is safe and clear access to all LSA / FFA,
- Packages should be stowed away from sunlight or other heat sources,
- No cargo should be stowed on top of portable tanks,
- Dg’s with give of vapour to be stowed on deck or in mechanically ventilated spaces,
- Cargo securing manual to be complied with Segregation as per the IMDG code.
Duties of Carrier & Shipper with respect to carriage of dangerous goods as per IMDG Code:
Under the IMDG (International Maritime Dangerous Goods) Code It is the onus of the shipper to determine the class of the substances according to provided criteria:-
- Stowage and segregation of dangerous goods:- Stowing and lashing the cargo are part of the operation of loading. It refers to the placing of the goods in a ship’s spot or a container. if there is an express contract or custom, stowage is done by the shipper. Chapter 7 of the IMDG Code contains detailed provisions regarding stowage and segregation of incompatible dangerous goods. Stuffing and sealing of the containers, is the responsibility of the shipper.
- Common Law:-
- To Pay Freight:- It is the shipper’s obligation to pay the freight agreed upon. The carrier has a lien on the cargo for unpaid freight.
- Not to ship dangerous goods without warning:- The shipper is responsible for notifying the carrier of any dangerous goods and is liable for failing to do so.
- To share in general average:- If a general average situation occurs the owner of the saved cargo and the carrier are obliged to jointly compensate the owner of the jettisoned cargo.
Explosives which may be Carried on Passenger Ships:
No other explosives may be transported on passenger ships except any one of the following:
- Explosive articles for life-saving purposes listed in the Dangerous Goods List, if the total net explosives mass of such articles does not exceed 50 kg per ship; or
- Goods in compatibility groups C, D and E, if the net explosives mass does not exceed 10 kg per ship; or
- Articles in compatibility group G other than those requiring special stowage, if the total net explosives mass does not exceed 10 kg per ship; or
- Articles in compatibility group B, if the total net explosives mass does not exceed 10 kg per ship.
SOURCE:- IMDG Code 7.1.7.5.2 Explosives in division 1.4, compatibility group S, may be transported in any amount on passenger ships.
Measures to be taken to Ensure a Safe Stowage and Carriage of Explosives:
- Stowage of dangerous goods on board container ships are decided by two factors, Document of Compliance and IMDG Code. IMDG Code sets forth the Stowage and Segregation Rules which is executed on each vessel according to the Document of Compliance issued to her. Document of Compliance is issued to a vessel if it meets the requirements of SOLAS Regulation II-2/19, Construction – Fire protection, fire detection and fire extinction (Carriage of Dangerous Goods).
- The Document of Compliance certifies that the construction and equipment of the mentioned ship have been found to comply with the provisions of regulation II-2/19 of the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea, 1974, as amended; and that the ship is suitable for the carriage of those classes of dangerous goods as specified in the appendix thereto, subject to any provisions in the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code and the International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargoes (IMSBC) Code for individual substances, materials or articles also being complied with.

ISO Tanks loaded on Vessel:
- In this document the under deck spaces and on deck spaces are marked separately for carriage of Packaged Dangerous Goods, Bulk Goods and what is not permitted.
- Validity of the document of compliance will not exceed 5 years and will not be extended beyond the expiry date of the valid Cargo Ship Safety Construction Certificate issued to the ship concerned under the provisions of SOLAS regulation I/12. See Maritime Safety Committee Circular MSC.1/Circ.1266 for full details.
- IMDG Code stowage and Segregation rules for dangerous goods vessels are categorized into two types, Cargo Ships and Passenger Ships. This categorization further divides cargo ships and passenger ships for carriage of Class 1, Explosives, and Classes 2 to 9. The differentiation is for Class 1, Explosives, Cargo ships (up to 12 passengers) and Passenger ships. For Classes 2-9 Cargo ships or passenger ships carrying a number of passengers limited to not more than 25 or to 1 passenger per 3 m of overall length, whichever is the greater number and Other passenger ships in which the limiting number of passengers transported is exceeded.
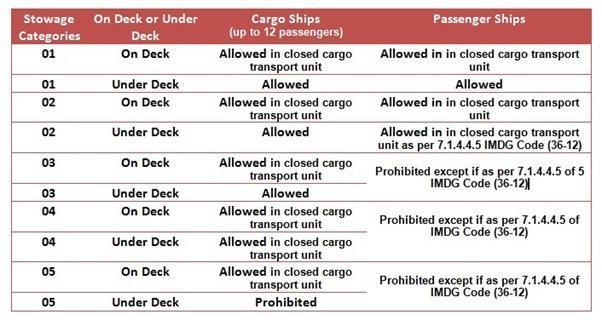
Stowage categories for Explosives (Class 1) – IMDG Code 36-12
- For other than class 1 (Explosives) each dangerous goods listed in IMDG Code 36th Amendment, Dangerous Goods List column 16 specifies stowage requirement. This is indicated by Category A, B, C, D or E.
- On Deck only stowage is always prescribed for cases where:
- Constant supervision is required; or
- Accessibility is particularly required; or
- There is a substantial risk of formation of explosive gas mixtures, development of highly toxic vapours, or unobserved corrosion of the ship
- Below dangerous goods when permitted to be loaded under deck by IMDG Code will additionally require mechanical ventilation for the cargo hold.
- class 2.1;
- class 3 with a flash point of less than 23°C c.c.;
- class 4.3;
- class 6.1 with a subsidiary risk of class 3;
- class 8 with a subsidiary risk of class 3, and
- dangerous goods to which a specific stowage requirement requiring mechanical ventilation in column 16 of the Dangerous Goods List is assigned.
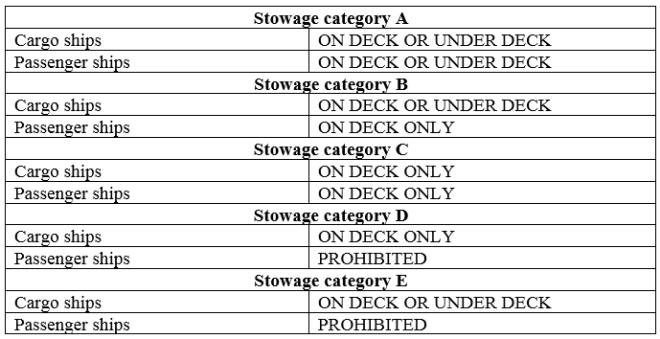
Stowage Categories for Goods other than Class 1 (Explosives)
- For example, UN 2076 Class 6.1 CRESOLS, LIQUID, stowage category in column 16 of dangerous goods list is Category B. Substances, Materials or Articles assigned with stowage Category B can be loaded on deck or under deck on a cargo ship but on a passenger ship where limiting number of passengers are exceeded Category B must be loaded on deck only!
- Segregation between containers carrying dangerous goods are different for containerships with closed cargo holds and hatchless containerships. Vertical and horizontal segregation, athwart ships, fore and aft is defined for Closed Versus Closed, Closed Versus Open and Open Versus Open.
- Two closed containers requiring segregation “separated from” each other when loading vertically or horizontally they need to be segregated as shown.
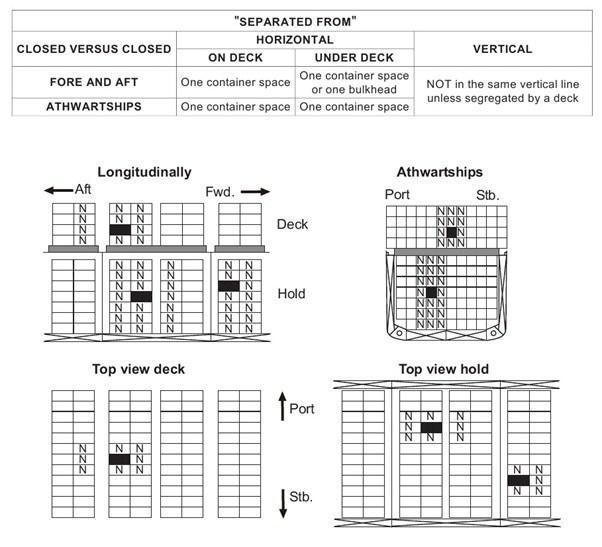
Two closed containers requiring segregation “separated from” each other when loading vertically or horizontally they need to be segregated as shown.
- In IMDG Code 37th Amendment Stowage and Handling instructions are listed separately in column 16a in Dangerous Goods List with SW and H codes and column 16b lists out segregation codes, SG.
IMDG Code: Subsidiary Risk Label:
- A subsidiary risk label shall also be affixed for any risk indicated by a class or division number in column 4 of the Dangerous Goods List of this Regulations;
- when there is no indication of a subsidiary risk in column 4, the special provisions in column 6 may also require or exempt a subsidiary risk label;
- Primary and subsidiary risk labels are required to be displayed next to each other;
- An explosive subsidiary risk label, division 1.1 must be applied for type B self-reactive substances;
- The class 5.2 label shall be affixed to packages containing organic peroxides classified as types B, C, D, E or F. In addition the following subsidiary risk labels shall be applied:
- For organic peroxides type B, the explosive subsidiary risk label division 1.1;
- If packing group I or II criteria of class 8 are met, the corrosive subsidiary risk label.
IMDG code: Stowage Category
- Positioning of dangerous goods containers on board vessels are categorised by ‘stowage categories’ to ensure safety. Many points are considered by IMDG Code for safe carriage of dangerous goods by sea-going vessels.
- On ships there are two different types of stowage (1) On deck and (2) Under Deck. When we look at a container vessel all those containers we see outside are stowed on deck. The containers stowed below the hatch covers are under-deck stowed units.
- For other than class 1 ( explosives ) ships are divided into two groups for this purpose
1) cargo ships or passenger ships carrying a number of passengers limited to not more than 25 or to 1 passenger per 3 m of overall length, whichever is the greater number;
2) Other passenger ships in which the limiting number of passengers transported is exceeded.
- For every dangerous goods listed in IMDG Code Dangerous Goods List column 16 specifies stowage requirement. This is indicated by Category A, B, C, D or E.
- On Deck only stowage is always prescribed for cases where:
1. Constant supervision is required; or
2. Accessibility is particularly required; or
3. There is a substantial risk of formation of explosive gas mixtures, development of highly toxic vapours, or unobserved corrosion of the ship
Below is the entry for UN 2076 Class 6.1 CRESOLS, LIQUID, you can see in column 16 it is written Category B. Substances, Materials or Articles assigned with stowage Category B can be loaded on deck or under deck on a cargo ship but on a passenger ship where limiting number of passengers are exceeded Category B must be loaded on deck only.
| Stowage category A | |
| Cargo ships or passenger ships carrying a number of Passengers limited to not more than 25 or to 1 passenger per 3 m of overall length, whichever is the greater number | ON DECK OR UNDER DECK |
| Other passenger ships in which the limiting number of passengers transported is exceeded | ON DECK OR UNDER DECK |
| Stowage category B | |
| Cargo ships or passenger ships carrying a number of passengers limited to not more than 25 or to 1 passenger per 3 m of overall length, whichever is the greater number | ON DECK OR UNDER DECK |
| Other passenger ships in which the limiting number of passengers transported is exceeded | ON DECK ONLY |
| Stowage category C | |
| Cargo ships or passenger ships carrying a number of passengers limited to not more than 25 or to 1 passenger per 3 m of overall length, whichever is the greater number | ON DECK ONLY |
| Other passenger ships in which the limiting number of passengers transported is exceeded | ON DECK ONLY |
| Stowage category D | |
| Cargo ships or passenger ships carrying a number of passengers limited to not more than 25 or to 1 passenger per 3 m of overall length, whichever is the greater number | ON DECK ONLY |
| Other passenger ships in which the limiting number of passengers transported is exceeded | PROHIBITED |
| Stowage category E | |
| Cargo ships or passenger ships carrying a number of passengers limited to not more than 25 or to 1 passenger per 3 m of overall length, whichever is the greater number | ON DECK OR UNDER DECK |
| Other passenger ships in which the limiting number of passengers transported is exceeded | PROHIBITED |
IMDG Code: Compatibility between Explosives:
- Class 1 – Explosives, are considered compatible with each other if storing them or transporting them together will not increase the probability of an accident or if there is an accident the magnitude of the effects. For this purpose explosives are divided into various compatibility groups. Each group is denoted by an alphabet from A to L, N and S (letter I is not used).
Divisions of Class 1 Explosives:-
Division 1.1: substances and articles which have a mass explosion hazard
Division 1.2: substances and articles which have a projection hazard but not a mass explosion hazard
Division 1.3: substances and articles which have a fire hazard and either a minor blast hazard or a minor projection hazard or both, but not a mass explosion hazard
Division 1.4: substances and articles which present no significant hazard
Division 1.5: very insensitive substances which have a mass explosion hazard
Division 1.6: extremely insensitive articles which do not have a mass explosion hazard
Compatibility Groups and Classification Codes:-
| Compatibility group | Classification code | Description of substance or articles |
| A | 1.1A | Primary explosive substance |
| B | 1.1B1.2B1.4B | Article containing a primary explosive substance and not containing two or more effective protective features. Some articles, such as detonators for blasting, detonator assemblies for blasting and primers, cap-type, are included even though they do not contain primary explosives. |
| C | 1.1C1.2C1.3C1.4C | Propellant explosive substance or other deflagrating explosive substance or article containing such explosive substance |
| D | 1.1D1.2D1.4D1.5D | Secondary detonating explosive substance or black powder or article containing a secondary detonating explosive substance, in each case without means of initiation and without a propelling charge, or article containing a primary explosive substance and containing two or more effective protective features |
| E | 1.1E1.2E1.4E | Article containing a secondary detonating explosive substance, without means of initiation, with a propelling charge (other than one containing a flammable liquid or gel or hypergolic liquids) |
| F | 1.1F1.2F1.3F1.4F | Article containing a secondary detonating explosive substance with its own means of initiation, with a propelling charge (other than one containing a flammable liquid or gel or hypergolic liquids) or without a propelling charge |
| G | 1.1G1.2G1.3G1.4G | Pyrotechnic substance, or article containing a pyrotechnic substance, or article containing both an explosive substance and an illuminating, incendiary, tear- or smoke-producing substance (other than a water-activated article or one containing whitephosphorus, phosphides, a pyrophoric substance, a flammable liquid or gel, or hypergolic liquids) |
| H | 1.2H1.3H | Article containing both an explosive substance and white phosphorus |
| J | 1.1J1.2J1.3J | Article containing both an explosive substance and a flammable liquid or gel |
| K | 1.2K1.3K | Article containing both an explosive substance and a toxic chemical agent |
| L | 1.1L1.2L1.3L | Explosive substance or article containing an explosive substance and presenting a special risk (such as due to water-activation or presence of hypergolic liquids, phosphides or a pyrophoric substance) and needing isolation of each type |
| N | 1.6N | Articles containing only extremely insensitive detonating substances |
| S | 1.4S | Substance or article so packaged or designed that any hazardous effects arising from accidental functioning are confined within the package unless the package has been degraded by fire, in which case all blast or projection effects are limited to the extent that they do not significantly hinder or prohibit fire fighting or other emergency response efforts in the immediate vicinity of the package |
To check whether two explosives are compatible to be stored/transported together the transport regulation has a segregation table as shown below:-
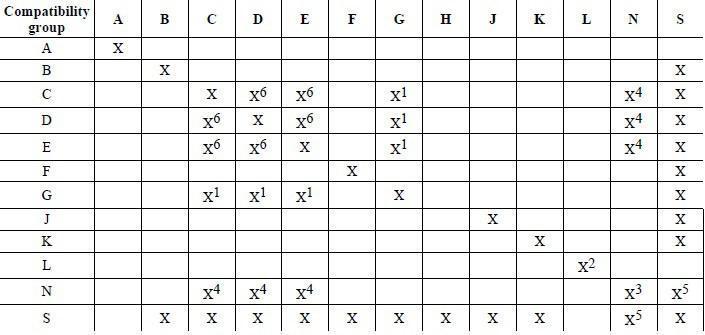
Notes for above table:-
“X” indicates that goods of the corresponding compatibility groups may be stowed in the same compartment, magazine, cargo transport unit or vehicle.
Notes:
- Explosive articles in compatibility group G (other than fireworks and those requiring special stowage) may be stowed with explosive articles of compatibility groups C, D and E provided no explosive substances are transported in the same compartment, magazine, cargo transport unit or vehicle.
- A consignment of one type in compatibility group L shall only be stowed with a consignment of the same type within compatibility group L.
- Different types of articles of Division 1.6, compatibility group N, may only be transported together when it is proven that there is no additional risk of sympathetic detonation between the articles. Otherwise they shall be treated as Division 1.1.
- When articles of compatibility group N are transported with articles or substances of compatibility groups C, D or E, the goods of compatibility group N shall be treated as compatibility group D.
- When articles of compatibility group N are transported together with articles or substances of compatibility group S, the entire load shall be treated as compatibility group N.
- Any combination of articles in compatibility groups C, D and E shall be treated as compatibility group E. Any combination of substances in compatibility groups C and D shall be treated as the most appropriate compatibility group shown in 2.1.2.3 of IMDG Code, taking into account the predominant characteristics of the combined load. This overall classification code shall be displayed on any label or placard placed on a unit load or cargo transport unit as prescribed in 5.2.2.2.2 of IMDG Code.
Example compatibility check:-
With the above table let us check segregation requirement between below two explosives:-
- UN 0161 Class 1.3C, POWDER, SMOKELESS
- UN 0191 Class 1.4G, SIGNAL DEVICES, HAND
Segregation between compatibility letters C and G shows X1 and as per note x1 explosive articles of group G ( UN 0191 in this case) may be stowed with explosive articles of group C, D and E provided no explosive substances are loaded in the same container, UN 0161 is a substance hence cannot be loaded with UN 0191.
Applicable sections of IMDG Code for compatibility groups and segregation within explosives please refer to section 2.1.2 & 7.2.7
Stowage and Segregation of Dangerous Goods on General Cargo Ships:
- Flammable gases or flammable liquids having a flashpoint of less than 23°C c.c, must be stowed on deck only, unless otherwise approved by the Administration and must be stowed at least 3 m from any potential source of ignition. Here possible sources of ignition may include open fires, machinery exhausts, galley uptakes, electrical outlets and electrical equipment including those on refrigerated or heated cargo transport units unless they are of certified safe type. For interpreting what is certified type, for cargo spaces, refer to SOLAS II:2/19.3.2 and for refrigerated or heated cargo transport units refer to Recommendation published by the international Electrotechnical Commission, in particular IEC 60079.
- When explosives are loaded the compartments or holds and containers must be locked to pervert unauthorized access however when in emergency access to the locked places must be able to be gained without delay. If the cargo compartment floors are not fitted with closed boarded wood the loading/unloading equipment and process must ensure no sparks can occur. If the cargo gets wet all handling operations must be stopped unless specialist advise from shipper clears same. Personnel involved in cargo operations must be briefed prior work regarding the potential risks and necessary precaution. When explosives belonging to different compatibility groups are loaded they must be stowed not less than 6 meters from each other unless mixed loading is permitted between the involved compatibility groups as per section 7.2.7 of IMDG Code.
- Non containerized flammable liquids packaged in plastics jerricans, plastics drums, plastics IBCs must always be stowed on deck. There are special requirements for stowage of FISHMEAL, UNSTABILIZED (UN 1374), FISHMEAL, STABILIZED (UN 2216, class 9) and KRILL MEAL (UN3497), SEED CAKE (UN 1386), AMMONIUM NITRATE BASED FERTILIZER, UN 2071 and certain other goods.
- When feeds or other edible substances intended for consumption by humans or animals, foodstuff, is loaded it will require segregation ‘separated from’ toxic, radioactive and corrosive dangerous goods and Dangerous goods in other classes which has segregation reference in column 16 (16b in 37th amendment of IMDG Code).
There are four segregation rules for dangerous goods loaded in conventional way on board ships:
- Away from: Effectively segregated so that the incompatible goods cannot interact dangerously in the event of an accident but may be transported in the same compartment or hold or on deck, provided a minimum horizontal separation of 3 metres, projected vertically is obtained.
- Separated from: In different compartments or holds when stowed under deck. Provided the intervening deck is resistant to fire and liquid, a vertical separation, i.e. in different compartments, may be accepted as equivalent to this segregation. For on deck stowage, this segregation means a separation by a distance of at least 6 metres horizontally.
- Separated by a complete compartment or hold from: Either a vertical or a horizontal separation. If the intervening decks are not resistant to fire and liquid, then only a longitudinal separation, i.e. by an intervening complete compartment or hold, is acceptable. For on deck stowage, this segregation means a separation by a distance of at least 12 metres horizontally. The same distance has to be applied if one package is stowed on deck, and the other one in an upper compartment.
- Separated longitudinally by an intervening complete compartment or hold from: Vertical separation alone does not meet this requirement. Between a package under deck and one on deck, a minimum distance of 24 m, including a complete compartment, must be maintained longitudinally. For on deck stowage, this segregation means a separation by a distance of at least 24 metres longitudinally.
Segregation rules between containerized dangerous goods and those loaded in conventional ways are different. Dangerous goods stowed in the conventional way must be segregated from goods transported in closed containers in accordance with segregation provisions showed above except that for “away from” is required, no segregation between the packages and the closed cargo transport units is required; and where “separated from” is required, the segregation between the packages and the closed cargo transport units may be as for “away from”.
Segregation between Bulk dangerous goods and packaged dangerous goods must be in accordance with the table shown in section 7.6.3.5.2 of IMDG Code where all 4 segregation terms have different rules from those listed above.
For full details of the requirements of stowage and segregation of dangerous goods loaded on general cargo ships refer to chapter 7.6 of IMDG Code, individual entries in chapter 3.2 and IMSBC Code as applicable.
IMDG code:- Types of packaging group
Packing groups indicate the level of danger and thus assist in selecting correct type of package for Dangerous Goods
There are three packing groups assigned in IMDG Code as below
Packing group I: substances presenting high danger;
Packing group II: substances presenting medium danger; and
Packing group III: substances presenting low danger
Classes 1, 2, 5.2, 6.2 and 7, and self-reactive substances of class 4.1 are not assigned with packing groups
Let us look at the criteria for assigning packing groups for each of the classes.
Class 1: Explosives – No Packing group assigned
Class 2: Gases – No Packing group assigned
Class 3: Flammable liquids – Flammable liquids are grouped for packing purposes according to their flashpoint, their boiling
point, and their viscosity.
Below table shows the relationship between flashpoint and boiling point
Packing Group.
| Flashpoint in °C closed cup (c.c.) | Initial boiling point in °C | |
| I II III | – < 23 ≥ 23 to ≤ 60 | ≤ 35 > 35 > 35 |
Viscous substances such as paints, enamels, lacquers, varnishes, adhesives and polishes having a flash point of less than 23 °C may be placed in packing group III in conformity with the procedures prescribed in part III, chapter 32.3, of the United Nations Manual of Tests and Criteria on the basis of:
- the viscosity, expressed as the flowtime in seconds;
- the closed-cup flashpoint;
- a solvent separation test.
Viscous flammable liquids such as paints, enamels, varnishes, adhesives and polishes with a flash point of less than 23 °C are included in packing group III provided that:
1) Less than 3% of the clear solvent layer separates in the solvent separation test;
2) The mixture or any separated solvent does not meet the criteria for class 6.1 or class 8.
3) The viscosity and flashpoint are in accordance with the following table:
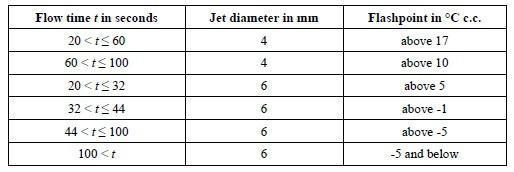
4) The capacity of the receptacle used does not exceed 30 ℓ.
Substances classified as flammable liquids due to their being transported or offered for transport at elevated temperatures are included in packing group III.
Class 4.1 Flammable solids
| Substance | Packing Group | Criteria |
| Readily combustible solids (other than metal powders) | II | If the burning time is less than 45 s and the flame passes the wetted zone |
| Powders of metal or metal alloys | II | if the zone of reaction spreads over the whole length of the sample in five minutes or less |
| Readily combustible solids (other than metal powders) | III | If the burning time is less than 45 s and the wetted zone stops the flame propagation for at leastfour minutes |
| Powders of metal | III | if the reaction spreadsover the whole length of the sample in more than five minutes but not more than ten minutes |
| Solids which may cause fire through friction | packing group shall be assigned by analogy with existing entries or in accordance with any appropriate special provision |
Class 4.2 – Substances liable to spontaneous combustion
Class 4.2 comprises Pyrophoric substances & Self-heating substances
| Substance | Packing Group | Criteria |
| Pyrophoric solids and liquids | I | Always Packing group I |
| Self-heating substances | II | which give a positive result in atest using a 25 mm sample cube at 140 °C |
| Self-heating substances | III | A positive result is obtained in a test using a 100 mm cube sample at 140 °C and a negative result is obtained in a test using a 25 mm cube sample at 140 °C and thesubstance is to be transported in packages with a volume of more than 3 m3;A positive result is obtained in a test using a 100 mm cube sample at 140 °C and a negative result is obtained in a test using a 25 mm cube sample at 140 °C, a positive result is obtained in a test using a 100 mm cube sample at 120 °C and the substance is to be transported in packages with a volume of more than 450 ℓ; A positive result is obtained in a test using a 100 mm cube sample at 140 °C and a negative result is obtained in a test using a 25 mm cube sample at 140 °C and a positive result is obtained in a test using a 100 mm cube sample at 100 °C. |
Class 4.3 – Substances which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases
| Packing Group | Criteria |
| I | any substance which reacts vigorously with water atambient temperatures and demonstrates generally a tendency for the gas produced to ignite spontaneously, or which reacts readily with water at ambient temperatures such that the rate of evolution of flammable gas is equal to or greater than 10 litres per kilogram of substance over any one minute. |
| II | any substance which reacts readily with water at ambienttemperatures such that the maximum rate of evolution of flammable gas is equal to or greater than 20 litres per kilogram of substance per hour, and which does not meet the criteria for packing group I. |
| III | any substance which reacts slowly with water at ambienttemperatures such that the maximum rate of evolution of flammable gas is equal to or greater than 1 litre per kilogram of substance per hour, and which does not meet the criteria forpacking groups I or II. |
Class 5.1 – Oxidizing substances
| Packing Group | Criteria |
| I | any substance which, in the 1:1 mixture (by mass) of substance andcellulose tested, spontaneously ignites; or the mean pressure rise time of a 1:1 mixture (by mass) of substance and cellulose is less than that of a 1:1 mixture (by mass) of 50% perchloric acid and cellulose; |
| II | Packing group II: any substance which, in the 1:1 mixture (by mass) of substance and cellulose tested, exhibits a mean pressure rise time less than or equal to the mean pressure rise time of a 1:1 mixture (by mass) of 40% aqueous sodium chlorate solutionand cellulose; and the criteria for packing group I are not met; |
| III | any substance which, in the 1:1 mixture (by mass) of substance and cellulose tested, exhibits a mean pressure rise time less than or equal to the mean pressure rise time of a 1:1 mixture (by mass) of 65% aqueous nitric acid and cellulose; and the criteria for packing groups I and II are not met; |
| Not Classified as 5.1 | any substance which, in the 1:1 mixture (by mass) ofsubstance and cellulose tested, exhibits a pressure rise of less than 2070 kPa gauge; or exhibits a mean pressure rise time greater than the mean pressure rise time of a 1:1 mixture (by mass) of 65% aqueous nitric acid and cellulose. |
Class 5.2 – Organic peroxides
No Packing group assigned
Class 6.1 – Toxic substances
Grouping criteria for administration through oral ingestion, dermal contact and inhalation of dusts and mists
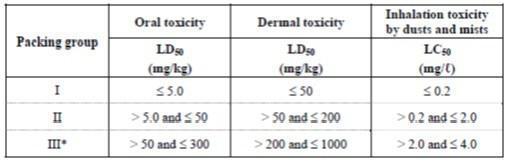
Tear gas substances shall be included in packing group II even if their toxicity data correspond to packing group III values.
Liquids having toxic vapours:
Liquids having toxic vapours shall be assigned to the following packing groups, where “V” is the saturated vapour concentration in mℓ/m3 air at 20 °C and standard atmospheric pressure:
Packing group I: If V ≥ 10 LC50 and LC50 ≤ 1,000 mℓ/m3.
Packing group II: If V ≥ LC50 and LC50 ≤ 3,000 mℓ/m3, and do not meet the criteria for packing group I.
Packing group III: If V ≥ 5/1 LC50 and LC50 ≤ 5,000 mℓ/m3, and do not meet the criteria for packing groups I or II.
Tear gas substances shall be included in packing group II even if their toxicity data correspond to packing group III values.
Class 6.2 – Infectious substances
No Packing group assigned
Class 7 – Radioactive material
No Packing group assigned
Class 8 – Corrosive substances
| Packing Group | Criteria |
| I | substances that cause full thickness destruction of intactskin tissue within an observation period of up to 60 minutes starting after an exposure time of 3 minutes or less |
| II | substances that cause full thickness destruction of intactskin tissue within an observation period of up to 14 days starting after an exposure time of more than 3 but not more than 60 minutes. |
| III | cause full thickness destruction of intact skin tissue within an observation period of up to 14 days starting after an exposure time of more than 60 minutes but not more than 4 hours; orare judged not to cause full thickness destruction of intact skin tissue but which exhibit a corrosion rate on either steel or aluminium surfaces exceeding 6.25 mm a year at a test temperature of 55 °C when tested on both materials. |
Class 9 – Miscellaneous dangerous substances and articles and environmentally hazardous substances
Some are assigned to Packing Group II and some to III.
Test methods for determining packing groups for each class are published in United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods-Manual of Tests and Criteria, as amended.


