Long Range Identification and Tracking (LRIT) system architecture Explanation:
Purpose of LRIT:-
- The Long Range Identification and Tracking (LRIT) system is a designated International Maritime Organization (IMO) system designed to collect and disseminate vessel position information received from IMO member States ships.
- The main purpose of the LRIT ship position reports is to enable a Contracting Government to obtain ship identity and location information in sufficient time to evaluate the security risk posed by a ship off its coast and to respond, if
necessary, to reduce any risks. - LRIT has also become an essential component of SAR operations and marine environment protection.
- It is a satellite-based, real-time reporting mechanism providing almost worldwide coverage (Inmarsat Coverage) that allows unique visibility to position reports of vessels that would otherwise be invisible and potentially a threat.
CARRIAGE REQUIREMENT of LRIT :- Ships in international voyages
- Passenger ships
- Cargo ships over 300 t
- Mobile platforms
Ships fitted with AIS and sailing in sea A1 areas do not need to transmit LRIT data.
INFORMATION TRANSMITTED in LRIT :-
- Identity (Ship’s LRIT Identifier)
- Position (Lat/Long)
- Date and time (UTC)
UPDATE INTERVAL in LRIT:-
- Default value 6 hourly
- Update interval remotely selectable
- Minimum interval 15 min
- May be switched off by the Master under certain conditions
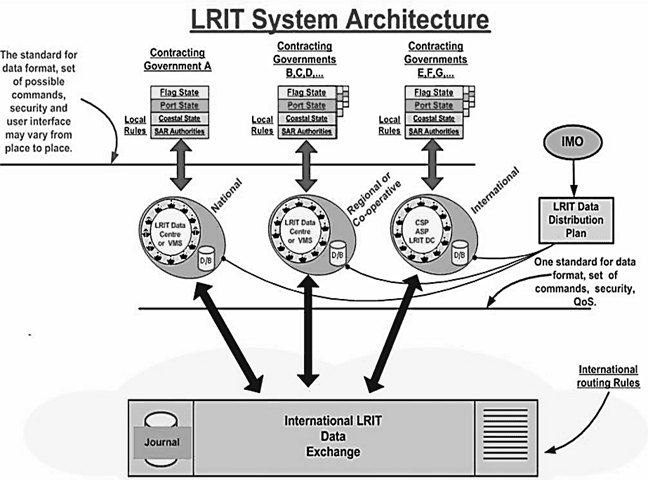
THE LRIT SYSTEM CONSISTS OF:
- The ship borne LRIT information transmitting equipment.
- Communications Service Providers (CSPs).
- Application Service Providers (ASPs).
- LRIT Data Centres (DC), including any related Vessel Monitoring System(s) (VMSs).
- The LRIT Data Distribution Plan (DDP).
- The International LRIT Data Exchange (IDE),
- LRIT coordinator
How does LRIT differ from AIS Explanation:
- Some confuse the functions of LRIT with that of AIS (Automatic Identification System), a collision avoidance system also mandated by the IMO, which operates in the VHF radio band, with a range only slightly greater than line-of-sight.
- (See AIS) While AIS was originally designed for short-range operation as a collision avoidance and navigational aid, it has now been shown to be possible to receive AIS signals by satellite in many, but not all, parts of the world. This is becoming known as S-AIS and is completely different from LRIT.
- The only similarity is that AIS is also collected from space for determining location of vessels, but requires no action from the vessels themselves except they must have their AIS system turned on.
- LRIT requires the active, willing participation of the vessel involved, which is, in and of itself, a very useful indication as to whether the vessel in question is a lawful actor.
- Thus the information collected from the two systems, S-AIS and LRIT, are mutually complementary, and S-AIS clearly does not make LRIT superfluous in any manner.
- Indeed, because of co-channel interference near densely populated or congested sea areas satellites are having a difficult time in detecting AIS from space in those areas.
Authorized receivers / users of LRIT
LRIT Data Centres:-
- The primary purposes of an LRIT Data Centre (DC) are to collect, store and make available to authorised entities the LRIT information transmitted by ships instructed by their administrations to utilise the services of that DC. In carrying out these core functions, the DC is required to ensure that LRIT data users are only provided with the LRIT information they are entitled to receive under the terms of SOLAS Regulation V/19.1.
- In addition, the LRIT DC acts as a “clearing house” by receiving requests for LRIT information lodged in other DCs from its associated Administration(s) and obtaining the data requested. Generally LRIT reports so requested will be exchanged through the International Data Exchange.
- LRIT Data Centers are required to archive their data so that the reports can be recovered, if required, at a later date and the activities of the DC can be audited by the LRIT Coordinator.
- LRIT DCs may make a charge for LRIT data they provide to other DCs.
- DCs may be either National (established to provide service to only one Contracting Government); Cooperative (established to provide services to a number of Contracting Governments) or Regional (established to provide services to a number of Contracting Governments acting through a regional entity of some kind).
The IMO Performance Standard envisages also an International Data Centre (IDC), to provide LRIT services on an international basis to many countries that do not wish to establish their own DCs, but the IMO Maritime Safety Committee (MSC) has not yet decided to establish such an IDC.
Functions of LRIT National Data Centre
- The International LRIT Data Exchange (IDE) exists to route LRIT information between LRIT DCs using the information provided in the LRIT Data Distribution Plan. It is therefore connected via the internet to all LRIT DCs and the LRIT Data
Distribution Plan server. - The IDE cannot access and does not archive the LRIT data itself, but it does maintain a journal of message header information – which can be understood as the “envelope” containing the LRIT information. This journal is used for invoicing functions and for audit purposes.
- The performance of the IDE is audited by the LRIT Coordinator.
How does LRIT differ from AIS?
Explanation:-
- AIS is a broadcast system and data is available to all receiver in the receiving range whereas LRIT is available only to the authorized person.
- AIS works on the very high frequency, whereas LRIT is based on the satellite system.
- AIS range is limited to the VHF range but LRIT range is worldwide.
- AIS DATA is not stored by any organization whereas LRIT data is stored and available on demand.
- There is display for AIS ON BOARD but there is no display for LRIT on board the ship.
Compare the AIS & LRIT:
| AIS | LRIT |
| Satellite | VHF |
| Global | Only where AIS coverage is provided |
| Secure Data | Public Data |
| Position, IMO Number, Date Time | Position, IMO Number, Date Time, Vessel Type, Speed, Course |
| Unlimited range | Line of sight, up to 40NM |
| Flag State Owns Data | Anyone can see data |
| Maritime Security and Awareness | Navigation and Anti-collision Tool |


